Extraction
aims to remove the tooth with a severe problem or not suitable to retain, or to prepare for another course of treatment like orthodontic treatment.
Outcome
Extraction is performed to remove teeth that have serious/underlying dental problems or that are not suitable to retain, or in conjunction with other dental treatments such as orthodontic treatment.
Conditions leading to extraction include:

A badly decayed/fractured tooth that cannot be restored
An extremely mobile tooth resulting from severe periodontal disease

A tooth to be extracted for pathological reasons, e.g. a tooth associated with tumor or the presence of supernumerary teeth
A tooth fails to erupt in a right place and causes damage and inflammation to the nearby tissues

A tooth that is abnormal in its appearance and structure/ to be extracted for orthodontic treatments
Extraction methods and procedures
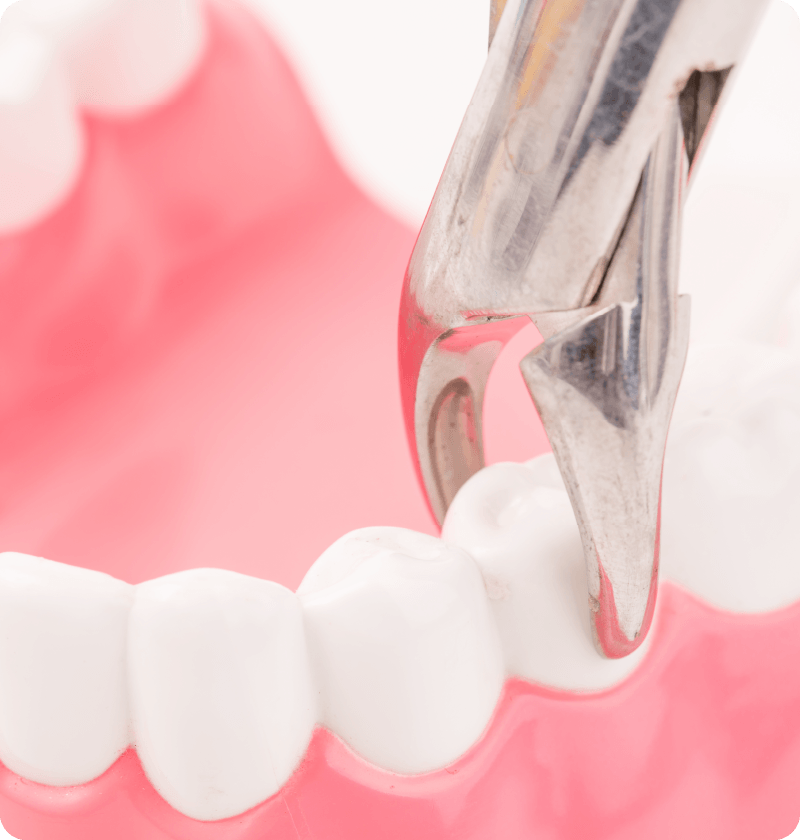
Non-surgical method
Generally, this is suitable for a normally erupted tooth. The dentist will give local anaesthesia to narcotize the tooth and surrounding tissues, appropriate dental instruments are used to loosen the tooth and extract out of the mouth. A cotton or gauze pack would be applied to the wound to stop bleeding after extraction.
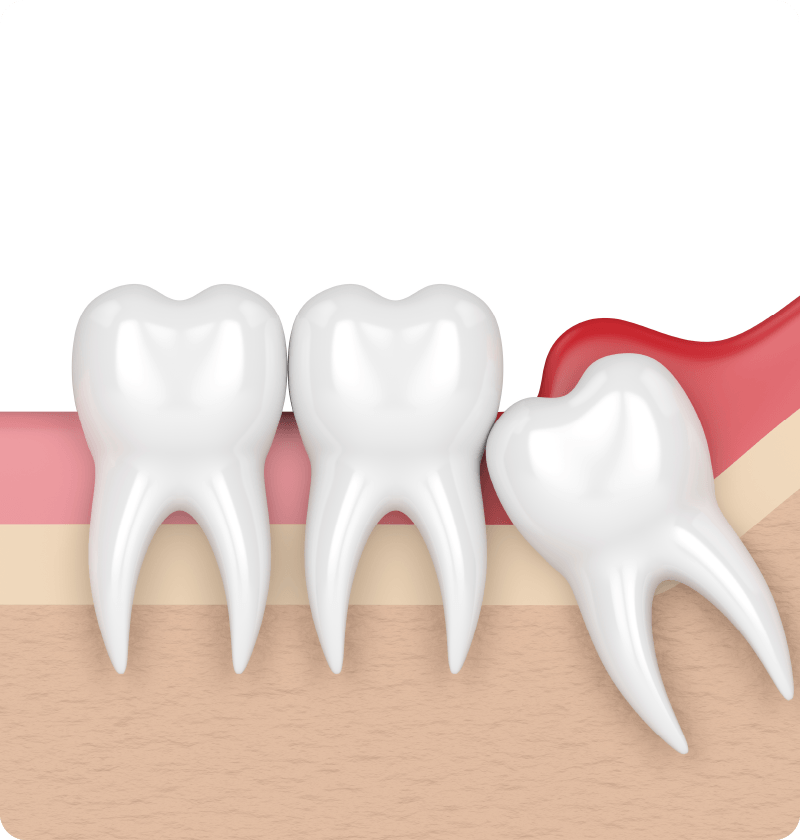
Surgical method
This is performed when the tooth cannot be simply extracted by the dental instruments, such as badly decayed/fractured tooth, impacted tooth (e.g. impacted wisdom tooth), crook-rooted tooth (which makes it difficult to be removed), tooth surrounded by very hard bone (common in the elderly), etc.
For surgical extractions, the dentist will first give local or general anaesthetic to narcotize the tooth and surrounding tissues. Reflect the gum to expose the bone, and then remove the covering bone to expose the roots. Loosen the tooth or cut the tooth into few parts and take them out one by one. Rinse and clean the wound, and close it up with sutures. A cotton or gauze pack would be applied to the wound to stop bleeding after extraction. Sutures would be removed after one or two weeks.
Post-extraction care to be taken:
Wound Care
- After extraction, bite on a gauze pack for 30 to 60 minutes to arrest bleeding from the tooth socket. To avoid bleeding from the socket again, the blood clot in it should not be touched or disturbed.
On the same day after extraction:
• Do not rinse the mouth • Do not touch the blood clot with the tongue or fingers
• Do not eat hard or rough food • Do not attempt vigorous exercise
- If there is profuse wound bleeding, the patient should immediately see his/her dentist or, depending on the bleeding severity, seek emergency care in the A&E of the nearby hospitals.
- As the tissues around the extraction site will be numb for some time, to avoid hurting them, do not bite or unduly touch those areas within 3 hours.
- It is normal to have some swelling at the wound, and it will subside in a few days. We may follow the dentist’s instructions to take the medication or use a cold pack to relieve it.
- Take the medication as instructed.
- After extraction, bite on a gauze pack for 30 to 60 minutes to arrest bleeding from the tooth socket. To avoid bleeding from the socket again, the blood clot in it should not be touched or disturbed.
On the same day after extraction:
• Do not gargle
• Do not touch the blood clot by the tongue or fingers
• Do not eat hard or rough food
• Do not attempt vigorous exercise
- If there is profuse wound bleeding, the patient should immediately see his/her dentist or, depending on the bleeding severity, seek emergency care in the A&E of the nearby hospitals.
- As the tissues around the extraction site will be numb for some time, to avoid hurting them, do not bite or unduly touch those areas within 3 hours.
- It is normal to have some swelling at the wound, and it will subside in a few days. We may follow the dentist’s instructions to take the medication or use a cold pack to relieve it.
- Take the medication as instructed.
Diet
- Avoid eating till the effect of local anaesthesia (temporary numbness in oral muscles) subsides.
- Avoid alcoholic or hot drinks
- In order to keep the wound clean, after 24 hours, rinse your mouth with warm saline for a few minutes after a meal.
Points to note for extraction:
- If the patients have other systemic diseases or taking medicines like anticoagulants or bisphosphonate (for treatment of osteoporosis or cancer), they should consult their medical doctors to check whether extraction should proceed or whether they need to take antibiotics, etc. in order to ensure extraction can be done safely.
- The dentist will assess and discuss with you the possible risks and benefits of tooth extraction. Generally, the risk of it is very low. The most common one is fracturing a tooth which may need surgical procedures to complete.
- It is normal to have mild discomfort in adjacent teeth for three to four days. So he/she should seek dentist help at once if the wound continues to have profuse bleeding, abnormal swelling, and even foul smell, pus running or if he/she has a fever.
- Potential complications and side effects include, but are not limited to pain and swelling, infection, bruising, limited mouth opening, temporary or permanent numbness of lip / tongue / chin / cheek / teeth, blood clot in vessels, bone fracture, allergic reaction, etc. As each individual case is different, please consult your dentist for details.
- Please contact the dentist or return to the hospital in case of difficulty in breathing, excessive bleeding, persistent nausea or vomiting, abnormal wound pain, swelling or fever.



 Clinic Location
Clinic Location



